Using the Windows 10-11 Task Manager for troubleshooting
This guide is to use the Windows 10-11 Task Manager for troubleshooting:
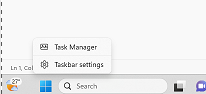
- To open the Task Manager, right-click on the taskbar and select “Task Manager” or just press “Ctrl + Shift + Delete” on your keyboard.
- The default view of the Task Manager window is the “Processes” tab, which displays a list of all the running processes on your system. You can sort the list by various criteria, such as the amount of CPU or memory usage.
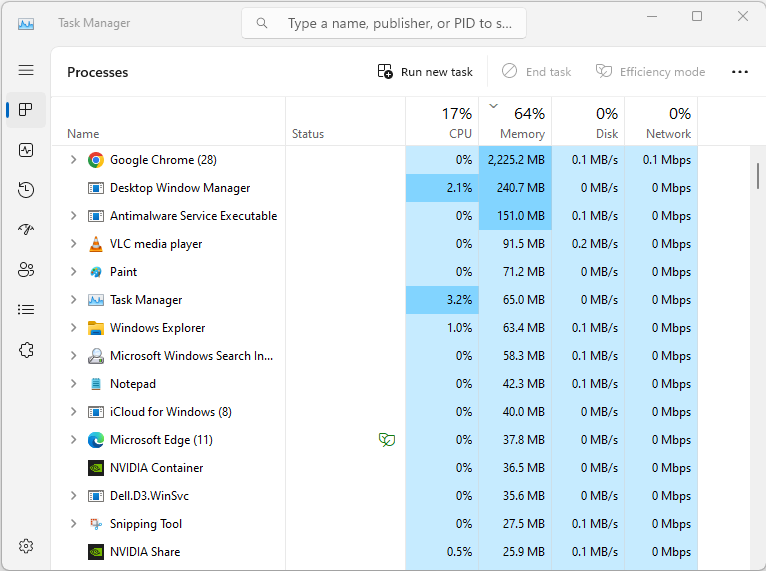
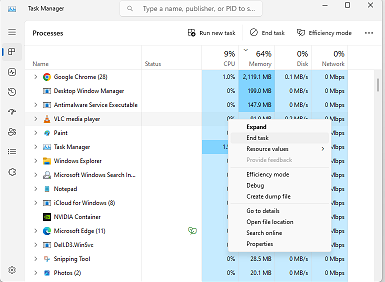
- If you notice that a particular process is consuming a lot of CPU or memory, you can right-click on it and select “End Task” to terminate it. Be careful when terminating processes as some may be critical to the operation of your system.
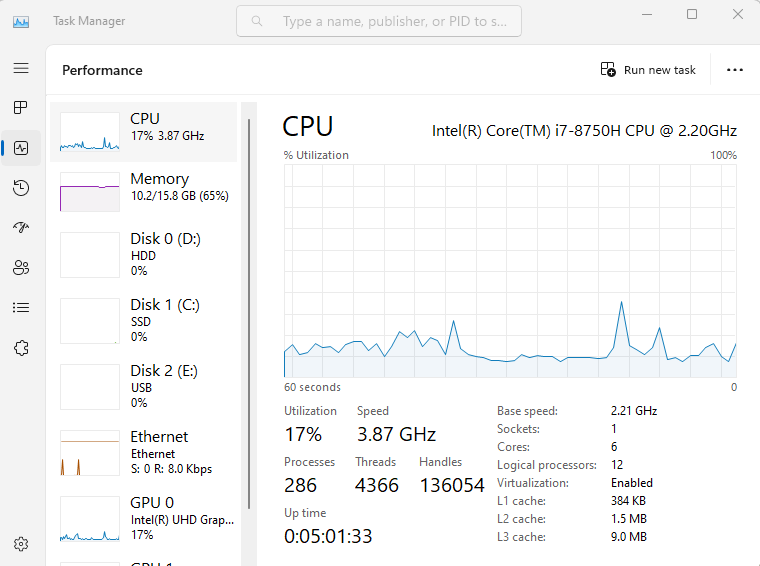
- The “Performance” tab displays real-time graphs for your CPU, memory, disk, and network usage. You can use this tab to monitor your system’s performance and identify any performance bottlenecks.
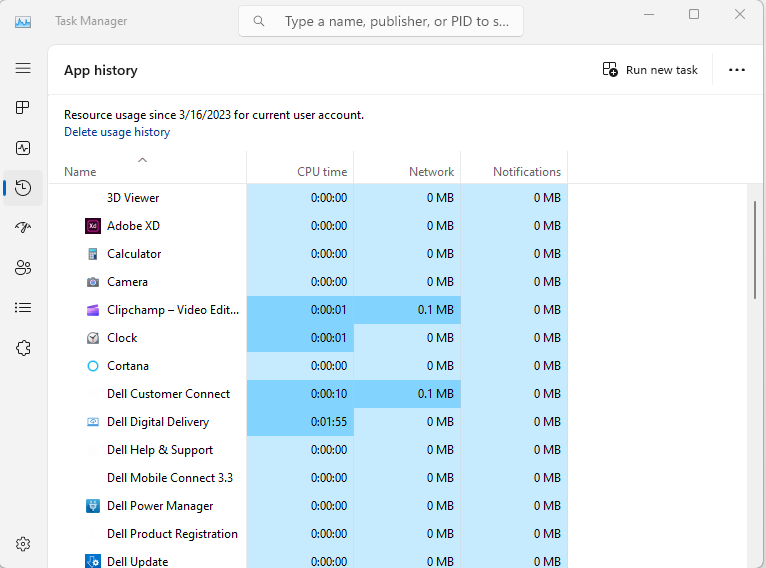
- The “App history” tab displays resource usage data for each app running on your system. You can use this tab to identify which apps are using the most resources.
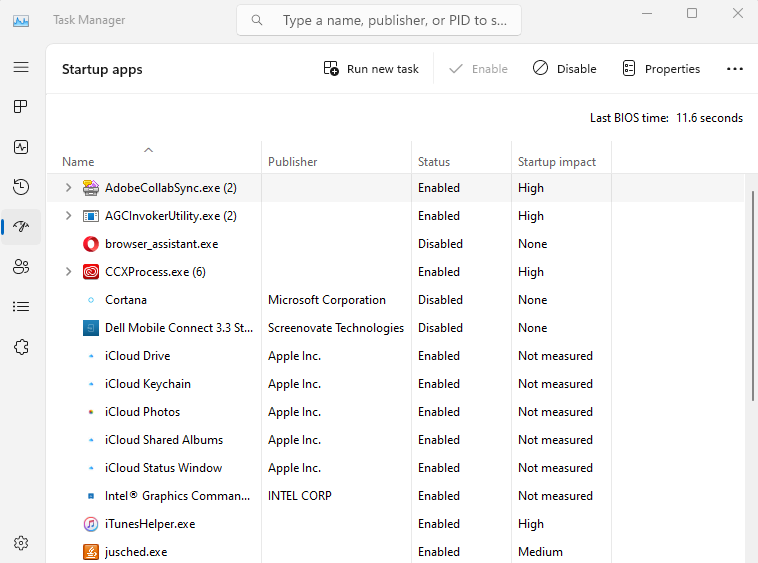
- The “Startup” tab displays a list of all the programs that are configured to run automatically when you start your system. You can disable any unnecessary programs to improve startup time and system performance.
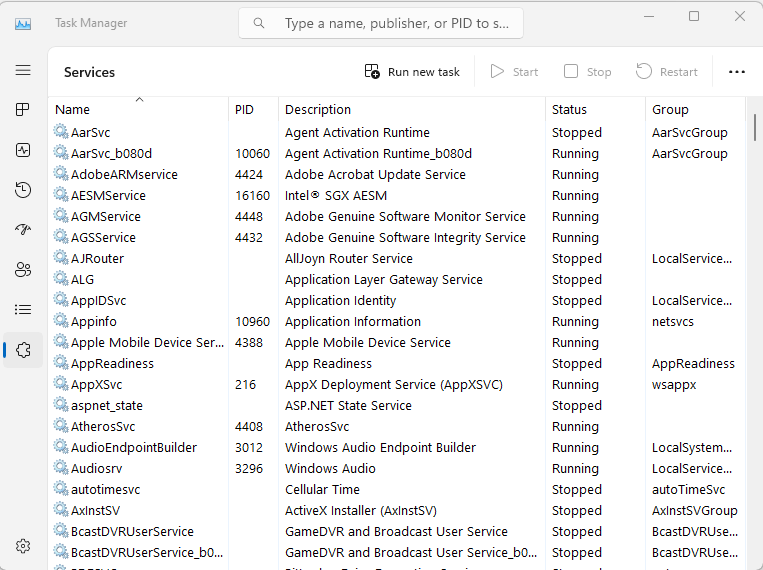
- The “Services” tab displays a list of all the system services running on your system. You can disable or stop any unnecessary services to improve system performance or troubleshoot issues.
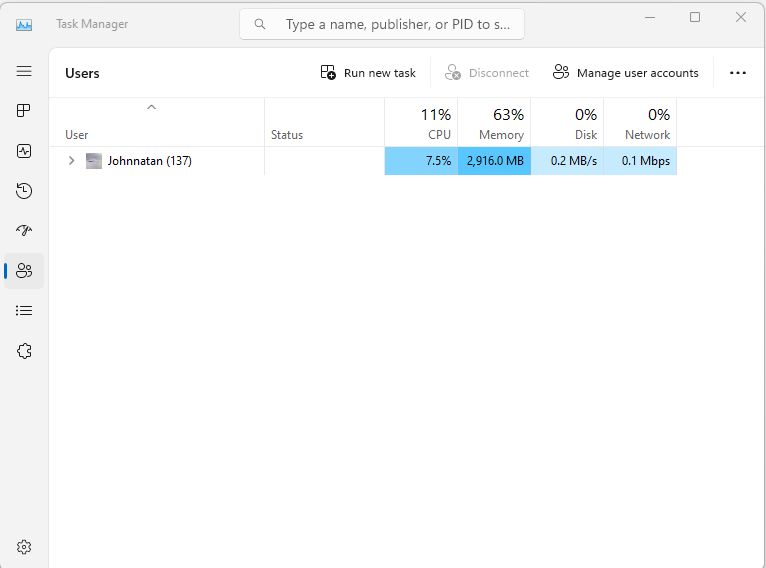
- The “Users” tab displays a list of all the users currently logged into your system. You can use this tab to identify any users that are consuming excessive resources or causing issues on your system.
You have now successfully used the Windows 10-11 Task Manager for troubleshooting.